 |
Bookmark | Contact Us |
 Technical support
Technical support
-
- Technical support
•Characteristics of Quartz Crystal
Quartz is a piezoelectric material was found to be one of the naturally occurring crystalline substance that exhibited the “piezoelectric” and being very stable, both chemically and mechanically, it became of great interest to the early electronic experimenters.
The chemical description of quartz is silicon dioxide Sio2. Although about 14% of the earth’s crust consists of Sio2, it occurs relatively infrequently in usable from with the necessary purity and lacking physical defects, cracks etc.
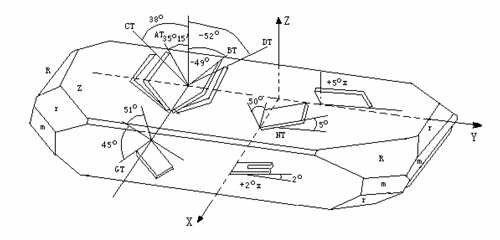
The crystal unit is an electronic device that is capable of composing a frequency generator circuit with an extremely high stability. It is used as oscillator and filter. The vibration and orientation angle shows in table1, which govern the characteristics of crystal unit, the equivalent circuit parameters, frequency temperature characteristics, load capacitance characteristics and frequency aging, etc. In these important characteristics from the standpoints of use, are described below.
•Mode of vibration
The vibration mode of thickness shear is usually using in field, the resonance frequency determined by the bland, such as AT&BT cut; in tuning fork mode which is determined by fork length of the blank. Table1 shows the relationship between the modes of. Vibration, cutting angle, frequency range, thickness or length and frequency and curvature constant which are determined by the mode of vibration.
Table1:
Quartz crystal vibration mod, cutting angle, frequency range & curvature constant.
•Equivalent Circuit
The resonant frequency of a quartz crystal is generally determined by the size of the plate combined with the mode in which it vibrates. The equivalent circuit of vibrating crystal is useful to explain the basic concept governing the crystal performance.
As show in Fig.2, the equivalent circuit of
crystal unit is represented by:
L1:Motional inductance (mechanical vibration)
C1:Motional capacitance (mechanical elasticity)
R1:Series resistance. (energy loss)
Co:Static capacitance.(which adds the stray capacitance of the holder to the static capacitance between the electrode in parallel)
•Characteristics of Load Capacitance
The load capacitance CL is the sum of capacitance of crystal socket or any other parasitic capacitance across the crystal in oscillation circuit, and a factor to determine the conditions of crystal unit when used in the oscillation circuit, the crystal is used in a range where it function as an inductive reactance. That means, when the oscillation circuit can be expressed as a series circuit of a negative resistance –R and a capacitance CL, the capacitance is called “Load capacitance”. The relationship between load capacitance and oscillation frequency is not linear. When the load capacitance is small, the amount of frequency variation is large, and when the load capacitance is increased, frequency variation lowers. If the load capacitance is lessened in the circuit to secure a large allowance for the oscillation frequency, the frequency stability will be greatly influenced even by a small change in the circuit.
•Equivalent Circuit Of Crystal Oscillation Circuit
When a crystal unit is actuated as an inductive reactance in an oscillator circuit, as Fig.4. To improve the starting conditions of the oscillation circuit, it is preferable to increase the value of negative resistance –R which parameter of the oscillation circuit. The starting conditions will be come worse if a circuit without much allowance in negative resistance (less negative resistance) is combined with a crystal unit having a larger resonance resistance. The oscillation circuit should be designed to a goal such that the value of negative resistance is 5 to 10 times the resonance resistance.
Fig.4:Equivalent Crystal Oscillation Circuit
•Frequency Vs Temperature
Characteristics of an T-Cut
Temperature coefficient is frequency stability or deviation with temperature change. The mode of vibration, the plane of the plate in relation to the axis of the quartz, the dimensions of the plate and harmonics determine the temperature coefficient.
The frequency-temperature characteristics of an AT-cut Crystal unit most generally used at present are expressed by cubic curves. As Fig.5, it displays excellent frequency stability over a wide temperature range. A Crystal plate is cut at an angle at which a required frequency tolerance is obtained in the given operation temperature range. Actually, there will have some dispersion in apparent cutting angle due to the result of cutting and polishing accuracy in the successive processes.
Copyright: Beijing Candor Electronics Co., Ltd.
Add:No.16, Yumin Street, Area B, Tianzhu Airport Industrial Zone,Beijing, P.R.China Postcode: 101318 Fax: +86-10-80483125
Tel: +86-10-80483105 (Ext.104, 105,107,113,118) E-mail: sale@mail.candor-co.com
